Heard the term ‘RTI’ tossed around in staff meetings? Let's cut through the jargon. At its heart, Response to Intervention (RTI) is a proactive framework for identifying and supporting students who are struggling with their learning.
It’s a powerful but simple idea: provide high-quality instruction to every student, and when someone struggles, act immediately. Think of it as a built-in academic safety net for your classroom, designed to catch kids before they fall too far behind.
What Is Response to Intervention Really About?
Instead of waiting for a student to fail before offering help, the RTI process uses data to catch learning gaps early. This allows us teachers to provide specific, targeted interventions right away. It's all about being proactive, not reactive.
The core mission is to solve small learning problems before they become big ones, ensuring every student gets the support they need to keep up with their peers.
The Shift from 'Wait-to-Fail'
To really get what RTI is, it helps to know what it replaced. For a long time, schools used a "discrepancy model" to identify learning disabilities. A student had to show a huge gap between their intellectual ability (IQ) and their actual academic performance.
This often meant waiting until second or third grade for a student to "fail enough" to finally qualify for support. It was a frustrating waiting game for teachers, parents, and especially the students themselves.
Response to Intervention flipped this script, emerging as a preferred method around 2004 with the reauthorization of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEIA). This change was driven by strong evidence showing that early, targeted support actually works. A major meta-analysis even found that RTI models have a significant positive impact on student outcomes. You can explore the full research on the effectiveness of RTI models to see the data for yourself.
The Big Idea: RTI is not just another initiative; it’s a fundamental change in how we think about student support. It ensures that a student's struggles are met with immediate, evidence-based help, not a waiting game.
Let's look at this shift more closely.
RTI at a Glance: Shifting from 'Wait-to-Fail' to Proactive Support
This table breaks down the key differences between the old way of thinking and the modern RTI framework. It highlights just how much our approach to supporting students has evolved for the better.
| Aspect | Traditional Approach ('Wait-to-Fail') | RTI Approach ('Proactive Support') |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Reactive: Wait for a significant failure to occur before intervening. | Proactive: Identify at-risk students early and provide immediate support. |
| Identification | Relies on a large gap between a student's IQ and achievement scores. | Uses universal screening and ongoing progress monitoring for all students. |
| Timing of Support | Delayed. Students often struggle for years before receiving help. | Immediate. Interventions begin as soon as a student shows signs of struggle. |
| Instruction | General, one-size-fits-all classroom instruction. | High-quality, evidence-based instruction for all, with differentiated tiers of support. |
| Data Use | Data is used primarily for a one-time eligibility decision for special education. | Data is used continuously to make instructional decisions and adjust interventions. |
| Focus | On labeling a student with a disability. | On providing the right support to help the student succeed in the general classroom. |
This proactive approach empowers educators to make a real difference the moment a need arises. It's about ensuring every student has the opportunity to succeed through a structured system of support that adapts to their individual learning journey.
Exploring the Three Tiers of RTI Support
The heart of Response to Intervention is its three-tiered model. Picture it as a pyramid—the broadest support is at the base, and the most intensive, one-on-one help is at the very top. This structure makes sure every student gets the right level of support right when they need it.
Let's borrow an analogy from the medical field. Think of the tiers like a doctor's approach to health: preventative care for everyone, specialized treatment for some, and intensive, critical care for a few. This shifts us away from a reactive "wait-to-fail" system and toward a proactive support network.
This image shows the shift from a traditional, reactive approach to the proactive safety net that RTI provides.
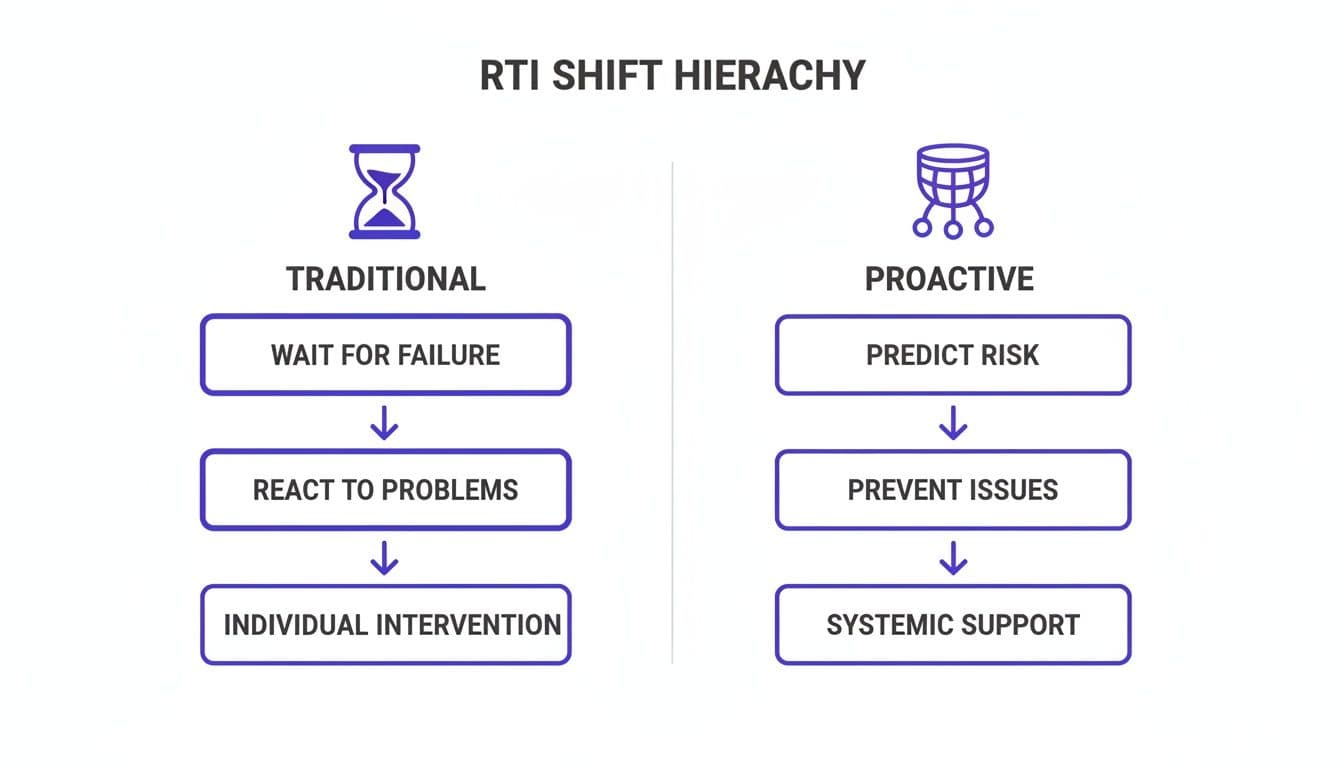
You can see how the traditional "hourglass" model lets many students slip through the cracks after initial instruction. In contrast, the RTI "safety net" is designed to systematically catch and support every struggling student.
Tier 1: The Foundation for All Students
Tier 1 is your classroom. It’s the high-quality, research-backed core instruction that all students get every single day. This is the bedrock of the entire RTI framework. The goal? For roughly 80-90% of students to find success with just this level of support.
But this tier is more than just delivering a great curriculum. It also includes universal screening—quick assessments given to all students to spot who might be at risk. These screeners are like a regular check-up, helping us catch potential issues before they grow.
Key Takeaway: Tier 1 isn't really an "intervention." It's the consistent delivery of excellent, evidence-based whole-class instruction and assessment that sets every student up for success.
To keep Tier 1 strong, you're constantly differentiating and using various formative assessment examples to check for understanding and adjust your teaching in the moment.
Tier 2: The Targeted Booster Shot
So, what happens if a student is still struggling in Tier 1? That’s where Tier 2 comes in. This tier provides focused, small-group instruction for the 5-10% of students who need an extra boost in a specific skill.
Think of it as a supplement, not a replacement. A Tier 2 student still joins in on all the core lessons with their peers but gets additional, targeted practice in an area like reading fluency or math facts.
These interventions are:
- Targeted: They zero in on a very specific, identified skill gap.
- Small-Group: Instruction is usually for just a handful of students with similar needs.
- Scheduled: Sessions are consistent, maybe three times a week for 30 minutes.
- Monitored: You track student progress often to see if the intervention is actually working.
Tier 3: The Intensive, Individualized Plan
For the small percentage of students (1-5%) who are still having a tough time even with Tier 1 and Tier 2 support, Tier 3 provides the most intensive and individualized help. This is the highest level of support within the general education system.
Here, instruction gets highly specific and is often delivered one-on-one or in a tiny group. The sessions are more frequent and last longer than in Tier 2, and the teaching is customized to the student's exact needs.
At this stage, data becomes even more crucial. Meticulous progress monitoring helps the school team—which might include you, specialists, and administrators—figure out if the student is responding. This data is also vital if a referral for a special education evaluation is eventually considered.
Ultimately, the tiered model ensures resources are used wisely. Instead of giving intensive help to everyone, RTI directs the strongest support to the few students who truly need it, all while strengthening the core instruction that benefits every child.
Putting RTI into Practice in Your Classroom
Alright, we've covered the theory behind the three tiers. But what does Response to Intervention actually look like on a rainy Tuesday morning when you've got a million things on your plate? This is where the rubber meets the road. It’s all about turning the RTI framework into practical, everyday actions that help your students thrive.
Let's break down what you can actually do at each tier without feeling like you need to completely overhaul your teaching style.

Making Tier 1 Work for Everyone
Tier 1 is your whole-class instruction, but it's so much more than just teaching from the front of the room. It’s about building a rock-solid foundation where the vast majority of your students can succeed. Think of it as your first, and most important, line of defense.
A huge piece of this is universal screening. This is like a quick academic check-up for all your students, typically done at the beginning, middle, and end of the year. It's not a high-stakes test, just a simple way to get a snapshot of who might need a bit more attention.
From there, it’s all about smart differentiation within your core lessons. This doesn't mean creating 30 different lesson plans. It just means offering different pathways to the same learning goal.
Here are a few practical ideas:
- Reading: During a whole-group lesson, you might offer some students sentence starters for their written responses, while others tackle a more complex text.
- Math: When teaching fractions, you could use hands-on manipulatives for learners who need a concrete visual, while others work on abstract word problems.
The secret to making this manageable is leaning on evidence-based teaching practices that are proven to work for a wide range of learners.
Implementing Tier 2 Small Group Interventions
When your data shows that a few students aren't quite getting a concept in Tier 1, it's time for Tier 2. This is your chance to pull a small group for focused, targeted support. The key here is to be strategic and efficient—you don't have time to waste.
These sessions should be short, frequent, and laser-focused on one specific skill. For instance, if a group is struggling with decoding CVC words, your Tier 2 intervention might be a 20-minute session, three times a week, dedicated solely to that skill.
Teacher Tip: Don't try to reinvent the wheel for every single intervention. Create a simple, repeatable routine for your small groups. This helps students know exactly what to expect and lets you focus your energy on instruction, not logistics.
Here are a couple of simple Tier 2 intervention ideas:
- Reading Fluency: Use "repeated readings," where a student reads a short passage multiple times with feedback to build speed and accuracy.
- Math Computation: Run targeted practice with flashcards or simple math games focused on specific facts, like multiplication tables.
Supporting Students in Tier 3
Tier 3 interventions are for the very few students who need intensive, individualized support. At this stage, you're definitely not working alone. This is where collaboration becomes absolutely essential.
You’ll be working closely with specialists like reading interventionists, special education teachers, or school psychologists. Your role is to provide the data from your classroom, help implement the strategies recommended by the team, and keep a close eye on the student's progress in the general education setting. For students who need specific communication support, understanding the role of child speech therapy can be an important part of putting together targeted interventions.
A huge part of making RTI work at any level is documentation and planning. This is where modern tools can be a game-changer. An AI assistant like Kuraplan can help you find standards-aligned activities, generate differentiated worksheets in seconds, and create assessments on the fly. Instead of spending your entire planning period hunting for the right resources, you can have them ready to go, freeing you up to focus on what matters most—your students.
Using Progress Monitoring to Guide Your Decisions
If the three tiers are the engine of RTI, then progress monitoring is the GPS. Without it, you’re just driving blind and hoping you end up at the right destination. This constant flow of data is what turns a good idea into a powerful, precise tool for helping every student succeed. It’s how you know if your efforts are actually working.
Progress monitoring isn't about adding another huge testing event to your schedule. It’s about frequent, quick check-ins that give you a clear picture of a student's growth over time. Think of it less like a final exam and more like taking a patient's temperature—it's a quick, simple way to see if an intervention is effective or needs an adjustment.
This process takes the mystery out of instructional decisions, replacing guesswork with confidence. You’ll have clear evidence to show what’s working, what isn’t, and exactly what to try next.
Choosing Your Tools and Timing
The key here is using the right tool for the job and checking in at the right frequency. Simply put, the intensity of your monitoring should match the intensity of the support a student is receiving.
- Tier 1: You're already doing this! Universal screeners (fall, winter, spring) and regular classroom assessments like chapter quizzes, exit tickets, and observations give you a pulse on the whole class.
- Tier 2: For students getting targeted help, you’ll need to check in more often. This usually means weekly or bi-weekly monitoring with a brief, focused assessment. A one-minute reading fluency probe or a quick math computation worksheet can give you the data you need in just a few minutes.
- Tier 3: At this most intensive level, monitoring is most frequent—often once or even twice a week. The data needs to be laser-focused on the student’s individual goals so you can make rapid instructional adjustments on the fly.
Making Sense of the Data
So, you have the data. Now what? The goal is to spot a trend. A simple line graph is often the best way to visualize a student's progress. Just plot the student's scores from each check-in, and you'll quickly see a story emerge from the numbers.
Is the line trending up, showing the student is closing the gap? Fantastic, your intervention is working. Is the line flat, showing the student has hit a wall? That’s your signal to make a change. For a deeper dive, check out these excellent data-driven instruction examples to see how you can turn numbers into actionable classroom strategies.
The Four-Point Rule: A common, teacher-friendly guideline is the "four-point rule." If you get four consecutive data points below the student's goal line, it's a clear signal that the current intervention isn't working and needs to be adjusted.
This simple rule stops you from sticking with a strategy that isn't helping a student. It empowers you to be responsive and agile in your teaching.
Knowing When to Adjust or Change Tiers
Your progress monitoring data is the driver behind every big decision in the RTI process. Based on the trends you see, you and your school's support team will follow a clear set of "decision rules."
Common Decision Rules:
- Continue the Intervention: If the data shows the student is making good progress and is on track to meet their goal, keep doing what you're doing. It’s working!
- Adjust the Intervention: If progress is slow or has stalled, it's time for a tweak. You might increase the intervention's frequency or duration, change the group size, or modify the instructional strategy itself.
- Move to a Different Tier: If a student in Tier 2 consistently smashes their goals, they may be ready to return to Tier 1 support. On the flip side, if a Tier 2 student doesn't respond after several adjustments, the team might decide to move them to a more intensive Tier 3 plan.
Making this whole process manageable often comes down to having the right resources ready to go. For instance, if you need to quickly adjust an intervention, a tool like Kuraplan can help you generate new, standards-aligned worksheets or activities in minutes. This lets you adapt your instruction based on real-time data without spending hours on prep, making data an ally instead of an obstacle.
Navigating RTI, MTSS, and Special Education
Once you get the hang of Response to Intervention, you'll start hearing other acronyms floating around, like MTSS and SPED. It’s easy to feel like you’re swimming in alphabet soup, but these systems are designed to work together to support every student.
Think of it less as a confusing jumble and more as a set of nested gears, all turning to move a child forward. The first thing to grasp is that RTI doesn't operate on its own island—it’s part of a much bigger picture.
The Connection Between RTI and MTSS
If you've heard the term Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS), you might be wondering if it's just a new name for RTI. Not exactly, but they are very close cousins. The easiest way to picture it is to think of MTSS as the big umbrella.
RTI focuses almost entirely on academics—helping kids who are struggling with reading, math, or other core subjects. MTSS, on the other hand, takes a whole-child approach. It includes all the academic support of RTI but also brings in support for social-emotional learning (SEL) and behavior.
So, while RTI is busy addressing a student's reading fluency, MTSS is designed to address that plus any attendance issues, behavioral challenges, or emotional hurdles that might be getting in the way of their learning.
- RTI: A multi-tiered model focused squarely on academic intervention.
- MTSS: A school-wide framework that includes RTI (academics) plus supports for behavior and social-emotional well-being.
Basically, if your school has a solid MTSS framework in place, you’re already doing RTI. It's the academic engine inside the larger MTSS vehicle.
Bridging RTI and Special Education
This is where the RTI process really shows its strength. Before RTI was common practice, the path to a special education referral was often paved by the "wait-to-fail" model. A student had to fall significantly behind their peers before we could even begin to offer serious help.
RTI completely flips that script. It gives us a rich, detailed story of a student's learning journey. The data you collect from progress monitoring in Tiers 2 and 3 isn't just for your records; it's critical evidence. It shows exactly what support was given, how the student responded, and every adjustment made along the way.
This data-driven approach ensures that a referral for special education is based on a student’s actual response to high-quality instruction, not just a single test score on a single day.
It makes the entire process more equitable and objective. It helps us figure out if a student truly has a learning disability or if they just needed a different instructional approach to click. Weeks of targeted intervention and careful monitoring paint a far clearer picture than a one-off evaluation ever could.
This body of evidence is invaluable for the Individualized Education Program (IEP) team. By the time a student is being considered for an evaluation, the team already has a wealth of information about what works and what doesn't for that specific learner. To better understand this evaluation process, you might find this guide on testing for special education helpful. This kind of deep, pre-existing knowledge makes the identification process far more accurate and fair for everyone involved.
Common RTI Challenges and How to Solve Them
Let's be real: implementing a Response to Intervention framework isn't always a walk in the park. Even with the best intentions, you’re going to hit bumps in the road. It’s important to talk about the common hurdles teachers face and find practical, classroom-tested ways to clear them.
One of the biggest struggles is simply finding the time. Between core instruction, grading, and a million other duties, carving out dedicated blocks for small-group interventions can feel impossible. Another huge pitfall is fidelity—making sure interventions are delivered consistently and as designed, which is tough when everyone is stretched thin.
And of course, there’s the resource crunch. Finding high-quality, evidence-based materials for very specific skill gaps can send you down a rabbit hole of late-night searching. These challenges are real, but they are definitely not unbeatable.
Finding Time in a Packed Schedule
Finding time for intervention isn't about adding more hours to your day; it's about getting creative with the time you already have. Many teachers find success by creating a dedicated "intervention block" or "WIN" (What I Need) time in their daily schedule.
This could be a 30-minute period after your ELA or math block where students dive into purposeful practice. While some students work on independent review or extension activities, you can pull your Tier 2 groups for that much-needed focused instruction. The key is to make this time sacred and consistent.
Teacher Tip: Use station rotations. One of your stations can be a teacher-led small group. This lets you meet with multiple groups of students each week while everyone else is engaged in meaningful, independent work.
Ensuring High-Fidelity Interventions
Consistency is everything. An intervention loses its power if it's applied sporadically or differently by various staff members. The first step is clarity: everyone on the team needs to understand the why and the how of each specific intervention strategy.
To solve this, lean on simple, clear protocols. Create a one-page summary for each intervention that outlines:
- The specific skill being targeted.
- A step-by-step guide to the activity.
- How often and for how long it should be done.
- The progress monitoring tool to be used.
This ensures that whether it's you, a paraeducator, or an interventionist, the student receives the same high-quality support every single time. The goal is to make the intervention predictable and powerful.
Overcoming the Resource Scramble
Scrambling to find the right materials for a specific intervention is a huge time-sink. This is where modern tools can be a lifesaver. Instead of starting from scratch every time, you can use an AI assistant to quickly find or create what you need.
For example, a platform like Kuraplan can help you find evidence-based strategies and generate differentiated worksheets, activities, and even assessments in minutes. By simply telling it the skill you're targeting, you get standards-aligned resources without the endless searching. This directly tackles the time and resource crunch, helping you implement Response to Intervention with fidelity and without the burnout.
Your Top RTI Questions Answered
Even with the best game plan, you're going to have questions as you start putting Response to Intervention into practice. It’s completely normal. Let’s walk through a few of the most common ones that pop up in the staff room.
How Is RTI Different From Just Good Teaching?
This is probably the most important question to ask. The short answer? RTI takes the principles of great teaching and wraps them in a systematic, data-driven framework.
Every great teacher naturally differentiates and helps kids who are falling behind. But RTI makes that process intentional and formal across the entire school. It’s the difference between intuitively knowing a student is struggling and using universal screeners to proactively find all students at risk, then using progress monitoring data to prove an intervention is actually closing the gap.
It’s less about guesswork and more about targeted, evidence-based support.
Do I Need to Be a Data Scientist to Do RTI?
Not at all. Seriously. The goal of RTI data isn't to bury you in spreadsheets; it's to give you clear, quick answers about what a student needs.
Often, progress monitoring is as simple as a one-minute reading fluency check or a quick math probe. Consistency is far more important than complexity. Think of yourself as a detective. The data points are just clues helping you figure out the next step for a student. Your school should give you the tools and tell you exactly what clues to look for.
The point of the data is to tell a clear story about a student's progress. It’s there to help you make confident decisions, not to create more work.
Can RTI Only Be Used for Reading and Math?
While RTI got its start fixing reading and math gaps in the early years, the model is flexible enough for just about anything—including writing and behavior.
The core idea is universal: provide high-quality instruction for everyone, monitor how they’re doing, and give targeted help to those who need it. This flexible approach is why it fits so perfectly inside the broader MTSS framework, which intentionally includes social-emotional and behavioral support.
Feeling the pressure to create differentiated materials for every tier? Kuraplan can generate standards-aligned lesson plans, worksheets, and assessments in minutes. Stop spending your nights and weekends searching for resources and get your time back. Learn more at Kuraplan.
